So, a straightforward explanation of the <wbr> tag in HTML stands for a work break. It doesn’t mean it will break every time but every time it needs to.
You might think, but CSS can do this using word-break: break-all, and yes, that will work, but we will have zero control.
To quickly show you the difference:

As you can see, the <wbr> version is way more readable because we control where it breaks! The CSS solution will break every time.
Of course, you can’t edit every content piece on your website, but I find this method super useful for headers!
How the HTML <wbr> tag works
It’s super easy to use this tag. We place it in the long word where it might have a breakpoint!
super<wbr />long<wbr />word<wbr />that<wbr />needs<wbr />to<wbr />break<wbr />better
You can see this is just a bogus word, but if we run this in our demo, you will see it breaks only on these points if it needs to!
It is an empty element meaning it doesn’t have an end tag and doesn’t need to self-close.
In the example above, we can have multiple breaks in one word.
Note: If you go smaller than the smallest breaks, it will not show!
Demo
I created this demo on Codepen to demonstrate the difference between the <wbr> HTML tag and the CSS word-break method.
You can resize these boxes horizontally to see the breakpoints.
See the Pen What is the <wbr> HTML tag and why do I need it? by Chris Bongers (@rebelchris) on CodePen.
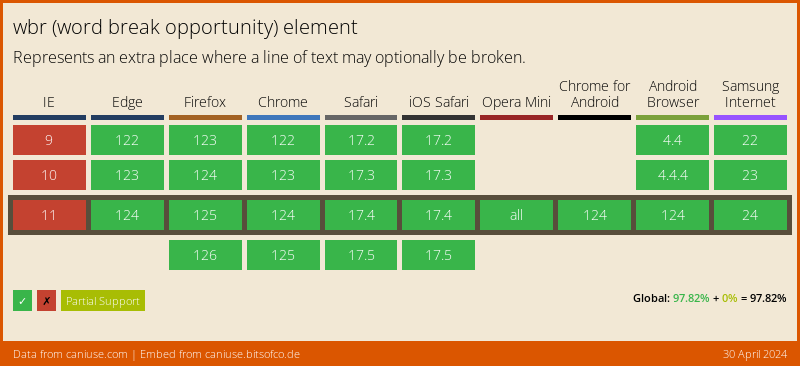
Browser Support
Full support!! Since IE is dead 💁♂️!
I like to use this super cool HTML attribute to fix minor responsive design issues.
Thank you for reading, and let’s connect!
Thank you for reading my blog. Feel free to subscribe to my email newsletter and connect on Facebook or Twitter