Docker is pretty awesome, and when creating a database instance with Docker, we can log in through the terminal command.
However, I’m one for graphic Database tools, so today I’ll guide you through how to connect to a Docker database.
Created the Docker database image
For this example, I’m going to use a MariaDB instance. The purpose of today is to show you how to connect with it.
Create a new docker-compose.yml file. This is the configuration file for Docker.
version: '3.7'
services:
db:
image: mariadb
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/mysql
ports:
- 3307:3306
environment:
MYSQL_DATABASE: my_db
MYSQL_USER: root
MYSQL_PASSWORD: root
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: root
volumes: db_data:
Above, we create a simple MariaDB image. I map the volume to a local folder (db_data). Furthermore, we set the environment to have some log-in possibility and a default database.
But the critical part for connecting is the ports!
The first number is the port we can connect to. We mustn’t use 3306 for this since this is our default system database.
I choose to use 3307 as it’s close to what we know.
You can, however, change this to anything that’s not in use.
Now when we run docker-compose up, we spool up this database.
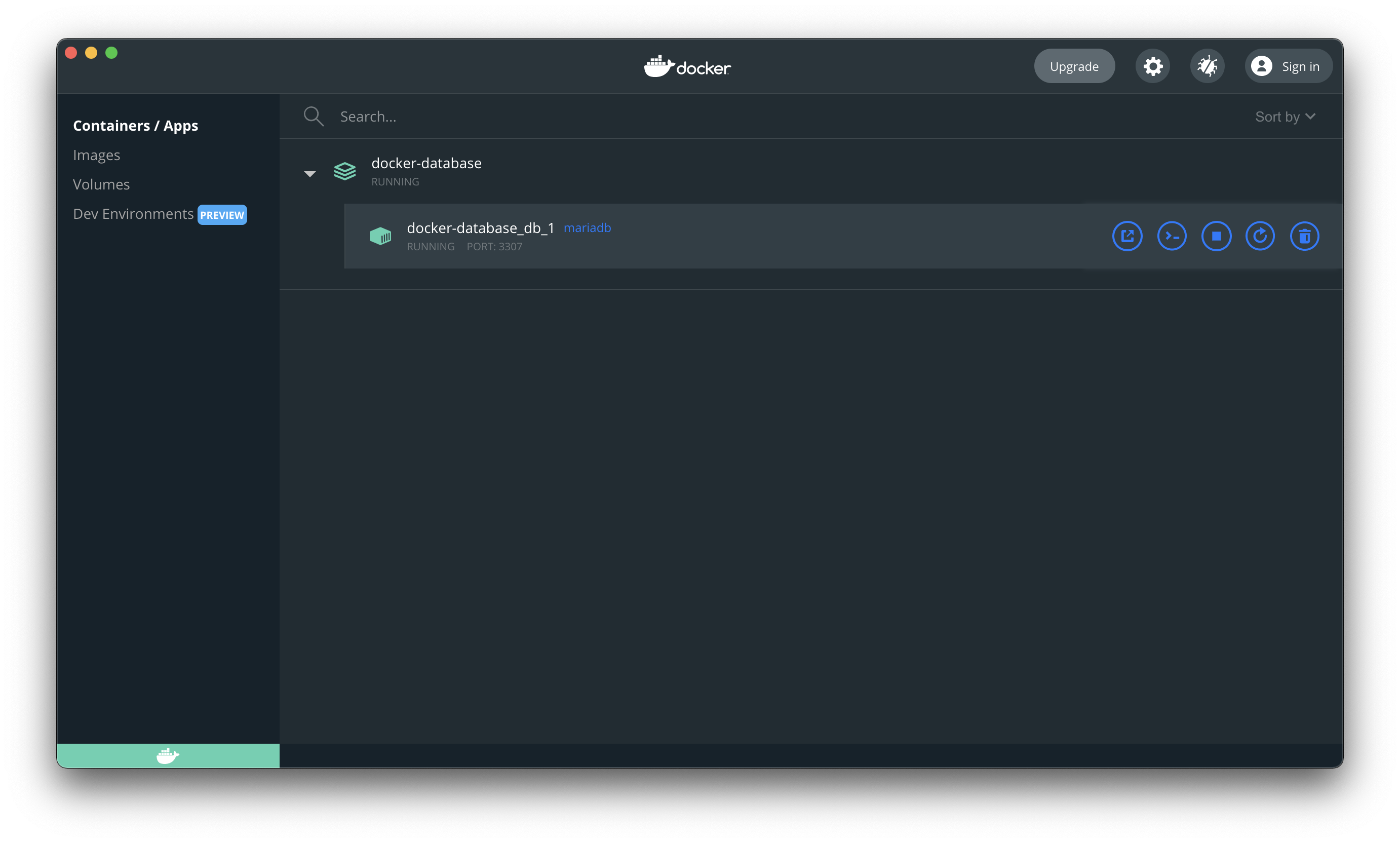
Connecting to the Docker database
Alright, let’s see how we can now connect to this, I’m using TablePlus, but the concept is the same for any tool.
We start by creating a new connection.
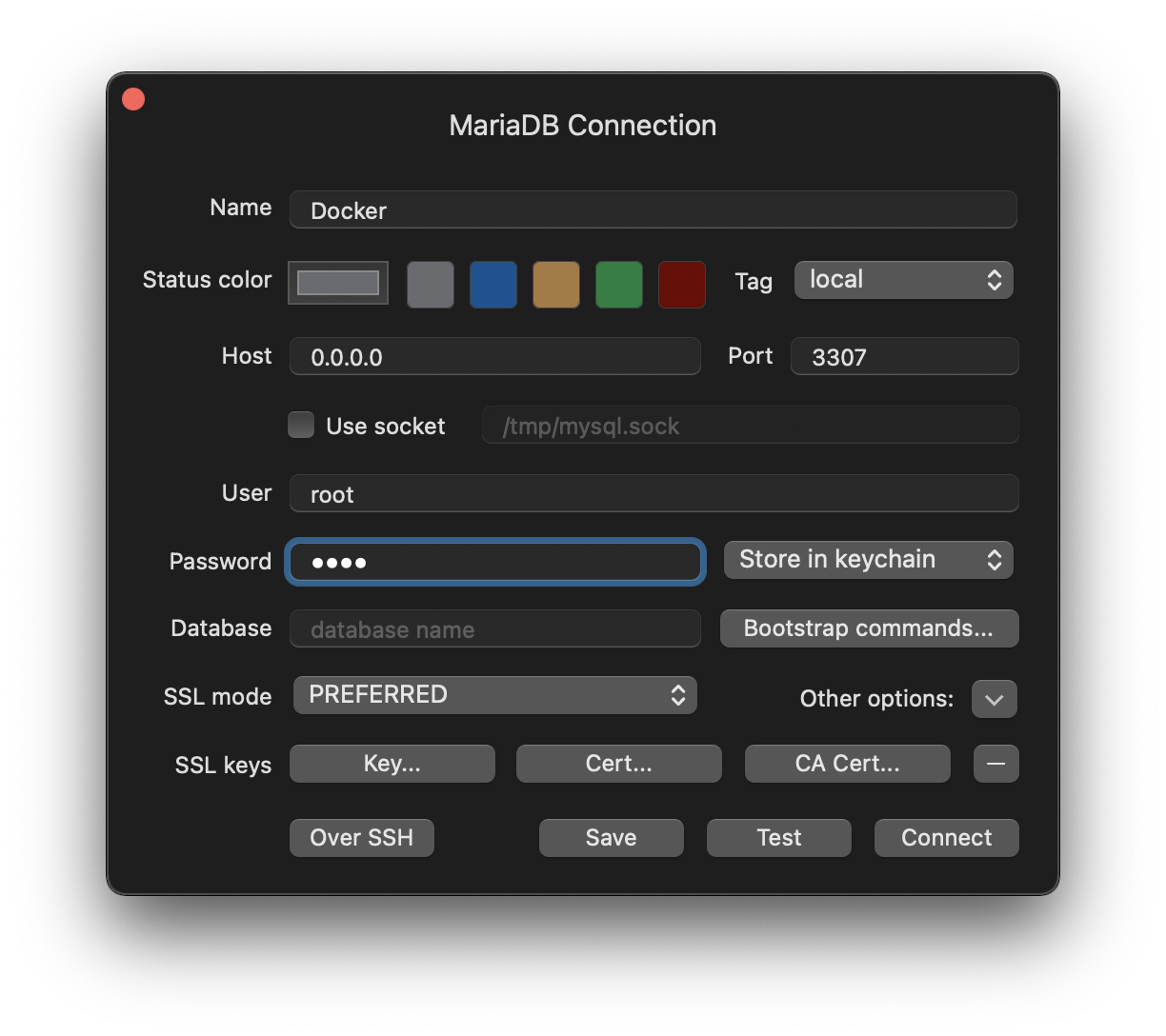
The main parts here are:
host: 0.0.0.0 as this will be the default docker hostport: 3307 as we described aboveuser: the user you set in the environmentpassword: the password set in the environment
Now you should be able to test and connect with the Docker database!
Thank you for reading, and let’s connect!
Thank you for reading my blog. Feel free to subscribe to my email newsletter and connect on Facebook or Twitter